Nursing Section
Procedures of Particle Beam Radiation Therapy
First Visit
- Patients should please get a referral from their primary care physician.
- The patient will receive an explanation from the doctor at HIBMC about whether particle beam radiation therapy is appropriate for his/her condition and what can be expected based on the medical information you bring to us.
- The patient's physical condition will be examined to see if he/she can meet the requirements for therapy. Depending on the patient, various treatment conditions may be required such as lying on the stomach, fasting, etc.
- Pre-treatment may be necessary, depending on the location of the illness. If the patient has a chronic condition such as diabetes or high blood pressure, he/she needs to consult his/her primary care physician before treatment to find out how to control his/her medical condition during radiation therapy.
- Some patients may be wary about the treatment because it is an advanced medical technology. We ask that the patient sort out the questions in advance so that we can use our treatment time efficiently.
- If the patient is hesitant about the treatment, it is important that he/she go back and talk it over thoroughly with the primary care physician and his/her family rather than making a hasty decision.
- If the patient has difficulty understanding the doctor's explanation or he/she has any concerns, it is advised to not hesitate to consult the nurse in charge. (Photo: Outpatient consultation)
- If the patient is accepted for the treatment, we will consult him/her about the date to start treatment preparations.
Return to the Center
- The patient's therapy goal is verified with the doctor. He/she explains the condition of the illness and the objective of the therapy, including whether the treatment will be a definitive cure of cancer or only an alleviation of the present condition.
- The doctor gives a description of the therapy and the side effects anticipated at this state.
- Preparations for the therapy begin. We set up a schedule ranging from examination to completion of therapy (a clinical path) - checkup, treatment, examination and nursing. (Photo: An explanation of clinical path by the doctor)
- The patient's goal is to be able to complete the entire therapy schedule as planned. Therefore, cooperation from the patient is indispensable.
- After the explanation from the doctor, guidance is given by the nurse and the radiation technologist.
Guidance from the Nurse
- The nurse will explain precautions in receiving the therapy and what the
patient can do proactively for himself/herself. (Photo: Path explanation
by nurse)
- As for the therapy schedule, as a general rule, treatments are administered
on weekdays, but depending on the equipment maintenance schedule, they
may also be done on Saturday.
- How the patient should spend the time during therapy period: Get plenty
of sleep and nutrients and be careful not to catch a cold.
- Health management: If the patient has any pre-existing chronic conditions,
he/she should let the nurse know about them.
- If the patient experiences pain or nausea, we will work with the patient
to find a way to alleviate these symptoms
- Anxiety can be a hindrance to treatment. If the patient feels anxious,
thisishould be freely communicated to us.
- For those who receive the therapy on an outpatient basis, we give precautionary
explanations about how to commute to HIBMC and what do to at home.
- The nurse will give explanations as to when the anticipated side effects
are most apt to happen, what to do to prevent them, and how to ease the
symptoms. These include:
Prostate …..Preventing inflammation of rectal mucous membrane, procedure to empty bladder, etc.
Head and neck …..Care of oral cavity, lockjaw, etc.
Prevention of dermatitis (skin irritation) ….. Preventive care, etc.
Guidance from the Radiation Technologist
The radiation technologist gives an explanation to each patient and shares
precautions regarding the actual exam and therapy. The patient's family
can participate together and ask questions.
Making the Immobilization Device
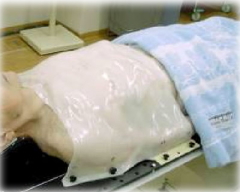 The particle beam radiation therapy is planned so that the tumor is killed effectively while minimizing the side effects from the radiation therapy. It is necessary to prevent slightest movements of the body .And an individual immobilization device is used to keep the irradiation region from moving. The actual positioning for the therapy is used in making the immobilization device, so the patient is urged to alert the staff if he/she has any problems or pain. The particle beam radiation therapy is planned so that the tumor is killed effectively while minimizing the side effects from the radiation therapy. It is necessary to prevent slightest movements of the body .And an individual immobilization device is used to keep the irradiation region from moving. The actual positioning for the therapy is used in making the immobilization device, so the patient is urged to alert the staff if he/she has any problems or pain.
(Photo: immobilization device)
CT and MRI Simulation
The basic images will be taken to prescribe the therapy.
Therapy Planning and Conference
- The therapy planning is carried out for the patient based on the images
obtained from the simulation images that show the tumor location, size,
and its relationship to surrounding organs.
- The planning is meticulously performed to have maximum kill of the tumor
while keeping collateral damage to the vital organs at a minimum.
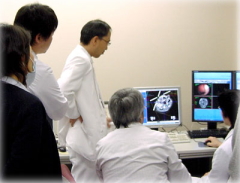 The plan prescribed individually for each patient is reviewed by doctors, radiation technologists, medical physicists, and nurses in the conferences. They exchange opinions as to whether the plan is right for the treatment goal and will garner the anticipated effect, whether all efforts are being made to minimize side effects, and if there are any problems pertinent to nursing care, etc. After all these points are discussed, the medical team reaches a consensus on the final irradiation exposure dose, number of fractions, the direction of the therapy, etc. The plan prescribed individually for each patient is reviewed by doctors, radiation technologists, medical physicists, and nurses in the conferences. They exchange opinions as to whether the plan is right for the treatment goal and will garner the anticipated effect, whether all efforts are being made to minimize side effects, and if there are any problems pertinent to nursing care, etc. After all these points are discussed, the medical team reaches a consensus on the final irradiation exposure dose, number of fractions, the direction of the therapy, etc.
(Photo: Conferences to discuss therapy)
Informed Consent
- While being shown the images for the prescribed therapy plan, the patient
receives an explanation of the therapy goal, specific irradiation methods,
and anticipated side effects.
- In radiation therapy, there are two types of side effects: ones that appear
during treatment to up to three months after the start of the therapy (an
acute-phase reaction), and others that begin after three months (a late-phase
reaction).
- With appropriate care, the former will recede after a while, but the latter
are difficult to heal, and can become a hindrance in the patient's daily
life. Efforts are made in the therapy plan to minimize the side effects,
but when they are unavoidable, it is important for the patient to fully
understand the explanations of these possibilities before receiving the
radiation therapy.
Rehearsal
- The patient will receive an information session regarding the therapy,
and his/her positioning will be confirmed so that the planned therapy can
be carried out precisely.
- We make every effort to make the patient comfortable during the course
of the therapy. If there is any pain, the patient is urged to communicate
with us.
- It is necessary to take measures to control conditions such as pain and
nausea before the therapy starts. The patient is advised to consult with
the doctors and nurses regarding medication use to alleviate these symptoms.
Therapy
- We support the patient so that he/she can receive the therapy most safely
and comfortably.
- If the patient has fever, feels fatigue, is unable to eat, or has swelling,
he/she should tell the nurse about it without fail.
- If for some unavoidable reason, the patient has become unable to receive
the therapy, he/she should let us know in advance.
- If the patient has any symptoms during the course of the therapy, he/she
should not fail to inform us.
Completion of Therapy and Informed Consent
- The doctor will give the patient an explanation about the therapy conducted,
what to expect, anticipated side effects, and post-therapy examinations
and tests.
 A personalized medical file, "the Patient Chart," will be given
to the patient. It has a summary of treatment and post-treatment plans.
(Photo: Patient Chart) A personalized medical file, "the Patient Chart," will be given
to the patient. It has a summary of treatment and post-treatment plans.
(Photo: Patient Chart)
- The nurse is present at this time. If there is something that the patient
does not understand, he/she should ask the nurse immediately.
- The nurse will give an explanation of the care that needs to be continued
after the therapy, the actual methods, and how to cope if there is an abnormality,
etc.
- There are individual differences in experiencing dermatitis (skin irritation)
and stomatitis (mouth ulcer), but the symptoms peak at around one month
after the therapy, and with appropriate care, they should get better in
about two months.
- If there is a nutritional deficient, or if the patient has pre-existing
chronic conditions such as diabetes, the healing may be delayed. It is
very important to keep the chronic medical conditions under control.
- An explanation will be given to the patient regarding how to detect early
the side effects that could occur more than three months after the therapy.
The patient is also informed of how to contact HIBMC for a consultation,
and where the consultation takes place.
Patient Follow-up
- After receiving particle beam radiation therapy, it is important for the
patient to visit the primary hospital to receive regular check-ups for
follow-up in order to detect relapse or metastasis at an early stage and
to confirm any side effects.
- After receiving the regular check-up examination at the primary hospital
after the particle beam radiation therapy, the patient sends the results
of the regular check-up and "the Patient Chart" to the HIBMC
Patient Follow-up Support Team.
 We offer advice on care methods and consultations for various concerns
regarding particle beam radiation therapy. We offer advice on care methods and consultations for various concerns
regarding particle beam radiation therapy.
●Patient Follow-up Support Team
Hyogo Ion Beam Medical Center
Patient Follow-up Support Team
1-2-1 Kouto, Shingu-cho, Tatsuno-shi, Hyogo
Phone: 0791-58-0100
FAX: 0791-58-2600
E-Mail:keika@hibmc.shingu.hyogo.jp |
|

 The particle beam radiation therapy is planned so that the tumor is killed effectively while minimizing the side effects from the radiation therapy. It is necessary to prevent slightest movements of the body .And an individual immobilization device is used to keep the irradiation region from moving. The actual positioning for the therapy is used in making the immobilization device, so the patient is urged to alert the staff if he/she has any problems or pain.
The particle beam radiation therapy is planned so that the tumor is killed effectively while minimizing the side effects from the radiation therapy. It is necessary to prevent slightest movements of the body .And an individual immobilization device is used to keep the irradiation region from moving. The actual positioning for the therapy is used in making the immobilization device, so the patient is urged to alert the staff if he/she has any problems or pain.  The plan prescribed individually for each patient is reviewed by doctors, radiation technologists, medical physicists, and nurses in the conferences. They exchange opinions as to whether the plan is right for the treatment goal and will garner the anticipated effect, whether all efforts are being made to minimize side effects, and if there are any problems pertinent to nursing care, etc. After all these points are discussed, the medical team reaches a consensus on the final irradiation exposure dose, number of fractions, the direction of the therapy, etc.
The plan prescribed individually for each patient is reviewed by doctors, radiation technologists, medical physicists, and nurses in the conferences. They exchange opinions as to whether the plan is right for the treatment goal and will garner the anticipated effect, whether all efforts are being made to minimize side effects, and if there are any problems pertinent to nursing care, etc. After all these points are discussed, the medical team reaches a consensus on the final irradiation exposure dose, number of fractions, the direction of the therapy, etc. A personalized medical file, "the Patient Chart," will be given
to the patient. It has a summary of treatment and post-treatment plans.
(Photo: Patient Chart)
A personalized medical file, "the Patient Chart," will be given
to the patient. It has a summary of treatment and post-treatment plans.
(Photo: Patient Chart)
 We offer advice on care methods and consultations for various concerns
regarding particle beam radiation therapy.
We offer advice on care methods and consultations for various concerns
regarding particle beam radiation therapy.