2.Particle Beam Radiation Therapy Planning
CT Imaging for Positioning
While the patient is in the posture to receive the particle beam radiation
therapy, we perform a CT scan to take cross-section images of the focus
area and its surroundings. These images become the key references for the
particle beam radiation therapy planning.
| 【1】 |
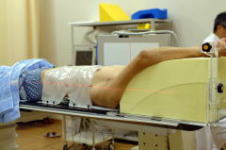
On the CT scan table, the patient takes the posture to receive the radiation
therapy and have the immobilization device attached. |
| 【2】 |
First, we mark the center point of the CT scan on the immobilization device
(marking). |
| 【3】 |
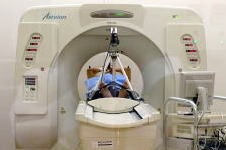
We take CT images. Unlike with tests performed for diagnostic purposes,
patients do not need to hold their breath. |
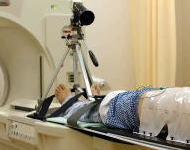
If the focus area of the treatment is in the chest or abdomen (lungs, liver, etc.), this area moves with the patient's breathing. Therefore, we use a respiratory gating system and collect CT images only at moments when the patient exhales. The patient is breathing freely, but it appears on the CT images as though he/she is holding his/her breath. (In the actual radiation treatment, the particle beam will be irradiated only at moments when the patient exhales, using the same respiratory gating system).
| 【4】 |
For positioning, we sometimes take matching images of the patient's front
and side. |
| 【5】 |
For the same purpose, we sometimes perform MRI scans as needed. |
 |
|
 |
| Attaching Immobilization Device |
|
Respiratory Sensor |
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
| CT Simulation |
|
Respiratory Gating System |
Particle Beam Radiation Therapy Planning
Using the CT images for positioning, a doctor evaluates the size and progression
of the tumor and makes a prescription for the appropriate particle beam
irradiation range, direction, and dose.
| 【1】 |
CT imaging does not always show the progression of the tumor clearly. If
necessary, we perform overlapping (fusion) of MRI and CT imaging of the
same area. |
| 【2】 |
Based on the images, we specify the progression of the tumor and define
the shape of the tumor on a computer. Taking into consideration errors
caused by the patient's respiration and body movement, we determine the
appropriate shape of the particle beam irradiation field. We also identify
the organs that might develop side effects. |
| 【3】 |
We determine the direction, energy, and depth of irradiation. Through a
series of trials on the computer, we select the most effective therapy
method that will minimize side effects. |
| 【4】 |
Lastly, we save and output the treatment planning data. |
 |
|
 |
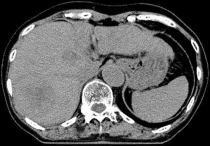
| Original CT Image for Positioning |
|
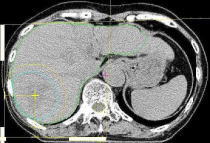
Specifying Tumor Shape |
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
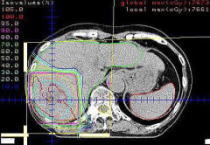
| 2D Dose Distribution Curves |
|
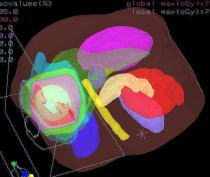
3D Dose Distribution Curves |
Therapy Planning Conferences (Morning Conference / Afternoon Conference)
The therapy plan that has been created is reviewed in the next Morning
Conference (attended by doctors, therapeutic radiation technologists, medical
physicists, and nurses). If they find a problem, they re-do the radiation
therapy planning. If the plan is approved, it is then submitted to the
Afternoon Conference, where it is re-checked and reviewed by any hospital
staff who missed the Morning Conference. Only after the plan is approved
in the Afternoon Conference is the therapy plan transferred to the particle
beam radiation therapy system.
 |
 |
| Morning Conference |
Afternoon Conference |
|










